4.3. Connecting to Public Cloud Storage via Acronis Backup Gateway¶
With Acronis Backup Gateway, you can have Acronis Backup Cloud or Acronis Backup Advanced store backups in a number of public clouds: Amazon S3, IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, IIJ, Cleversafe, Microsoft Azure, Swift object storage, Softlayer (Swift), Google Cloud Platform, as well as solutions using S3 with the older AuthV2-compatible authentication methods. However, compared to the local Acronis Storage cluster, storing backup data in a public cloud increases the latency of all I/O requests to backups and reduces performance. For this reason, it is recommended to use the local Acronis Storage cluster as storage backend.
Since backups are cold data with specific access rights, it is cost-efficient to use storage classes that are intended for long-term storage of infrequently accessed data. The recommended storage classes include the following:
- Infrequent Access for Amazon S3,
- Cool Blob Storage for Microsoft Azure,
- Nearline and Coldline Storage for Google Cloud Platform.
Note that real data storage costs may be 10-20% higher due to additional fees for operations like data retrieval and early deletion.
Important
- When working with public clouds, Acronis Backup Gateway uses the local storage as the staging area as well as to keep service information. It means that the data to be uploaded to a public cloud is first stored locally and only then sent to the destination. For this reason, it is vital that the local storage is persistent and redundant so the data does not get lost. There are multiple ways to ensure the persistence and redundancy of local storage. You can deploy Acronis Backup Gateway on multiple cluster nodes and select a good redundancy mode. If Acronis Storage with the gateway is deployed on a single physical node, you can make the local storage redundant by replicating it among local disks. If Acronis Storage with the gateway is deployed in a virtual machine, make sure it is made redundant by the virtualization solution it runs on.
- Make sure the local storage cluster has plenty of logical space for staging. For example, if you perform backup daily, provide enough space for at least 1.5 days’ worth of backups. If the daily backup total is 2TB, provide at least 3TB of logical space. The corresponding raw storage required will vary depending on the encoding mode: 9TB (3TB per node) in the mode 1+2, 5TB (1TB per node) in the mode 3+2, etc.
- You must update Acronis Backup Agents to version 12.0.4492 (Windows/Mac) or 12.0.4470 (Linux). Otherwise agents’ attempts to place backups in the new storage backend will result in “Backup failed” errors.
- If you are to store backups in an Amazon S3 cloud, keep in mind that Acronis Backup Gateway may sometimes block access to such backups due to the eventual consistency of Amazon S3. It means that Amazon S3 may occasionally return stale data as it needs time to render the most recent version of the data accessible. Acronis Backup Gateway detects such delays and protects backup integrity by blocking access until the cloud updates.
Before you proceed, make sure that the destination storage has enough space for backups.
To set up Acronis Backup Gateway, do the following:
In the left menu, click SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway.

Select node(s) to run the gateway services on and click Create gateway in the right menu.
Select Public Cloud as storage type.
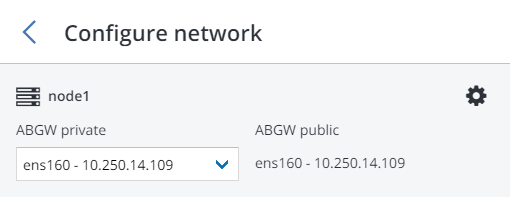
Make sure a network interface with the ABGW private role is selected in the drop-down list. The corresponding interfaces with the ABGW public role will be selected automatically. Click NEXT.
Note
If necessary, click the cogwheel icon and assign the required role(s) to network interfaces on the Network Configuration screen.
On the Public cloud parameters pane, do the following:
- Select a public cloud provider. If your provider is S3-compatible but not in the list, try AuthV2 compatible.
- Depending on the provider, specify Region, Authentication (keystone) URL, or Endpoint URL.
- In case of Swift object storage, specify the authentication protocol version and attributes required by it.
- Specify user credentials. In case of Google Cloud, select a JSON file with keys to upload.
- Specify the folder (bucket, container) to store backups in. The folder must be writeable.
Click NEXT.
On the Registration pane, specify the following information for your Acronis product:
- In Account Server Name, specify the address of the Acronis Backup Cloud management portal (e.g., https://cloud.acronis.com/) or the hostname/IP address and port of the Acronis Backup Advanced management server (e.g., http://192.168.1.2:9877).
- In Acronis Account, specify the credentials of a partner account in the cloud or of an organization administrator on the local management server.
Finally, click DONE.
