Connecting Acronis Backup Software to Storage Backends via Acronis Backup Gateway¶
The Acronis Backup Gateway storage access point (also called “gateway”) is intended for service providers who use Acronis Backup Cloud and/or Acronis Backup Advanced and want to organize an on-premise storage for their clients’ backed-up data.
Acronis Backup Gateway enables a service provider to easily configure storage for the proprietary deduplication-friendly data format used by Acronis.
Acronis Backup Gateway supports the following storage backends:
- Acronis Storage clusters with software redundancy by means of erasure coding,
- NFS shares,
- public clouds, including a number of S3 solutions as well as Microsoft Azure, OpenStack Swift, and Google Cloud Platform.
While your choice should depend on scenario and requirements, it is recommended to keep Acronis backup data in the local storage cluster. In this case, you can have the best performance due to WAN optimizations and data locality. Keeping backups in an NFS share or a public cloud implies the unavoidable data transfer and other overhead, which reduces overall performance.
Note
- When configuring Acronis Backup Gateway, you will need to provide the credentials of your administrator account in the Acronis backup software.
- In cases when not local but external storage (e.g., NFS) is used with Acronis Backup Gateway, redundancy has to be provided by said external storage. Acronis Backup Gateway does not provide data redundancy or perform data deduplication itself.
Understanding the Infrastructure¶
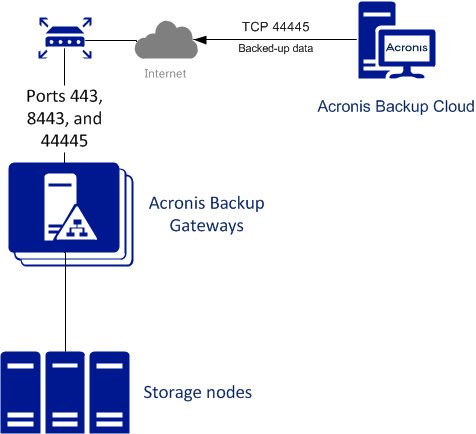
The Acronis Backup Gateway storage access point runs as services on the Acronis Storage nodes. It should be deployed on multiple Acronis Storage nodes for high availability.
Connecting to the Local Storage Cluster via Acronis Backup Gateway¶
Before you proceed, make sure that the destination storage has enough space for backups.
To set up Acronis Backup Gateway, do the following:
In the left menu, click SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway.

Select node(s) to run the gateway services on and click Create gateway in the right menu.
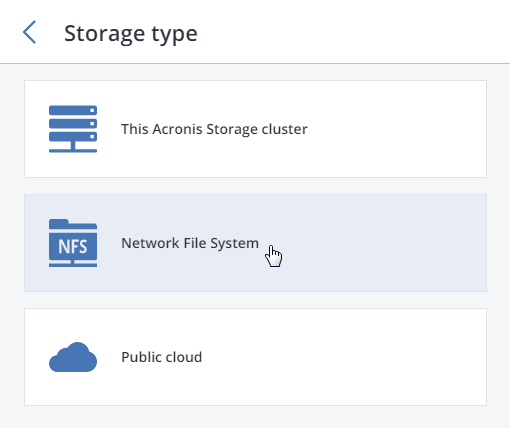
Select This Acronis Storage cluster as storage type.

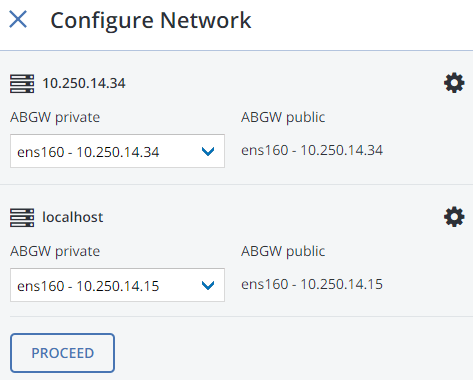
Make sure a network interface with the ABGW private role is selected in the drop-down list. The corresponding interfaces with the ABGW public role will be selected automatically. Click NEXT.
Note
If necessary, click the cogwheel icon and assign the required role(s) to network interfaces on the Network Configuration screen.
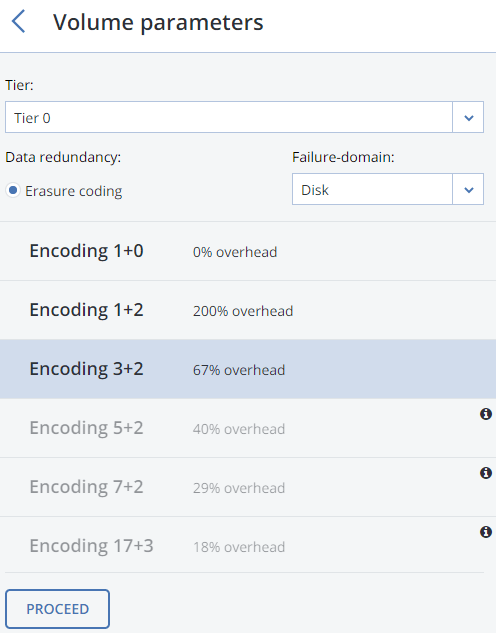
On the Volume Parameters tab, select the desired tier, failure domain, and data redundancy mode.
Note
- Redundancy by replication is not supported for Acronis Backup Gateway.
- You can later change the erasure coding mode on the Acronis Backup Gateway > Parameters panel.
On the DNS Configuration tab, specify the external DNS name for this gateway, e.g,
backupgateway.example.com. Make sure that each node running the gateway service has a port open for outgoing Internet connections and incoming connections from your Acronis backup software. Backup agents will use this address and port to upload the backup data.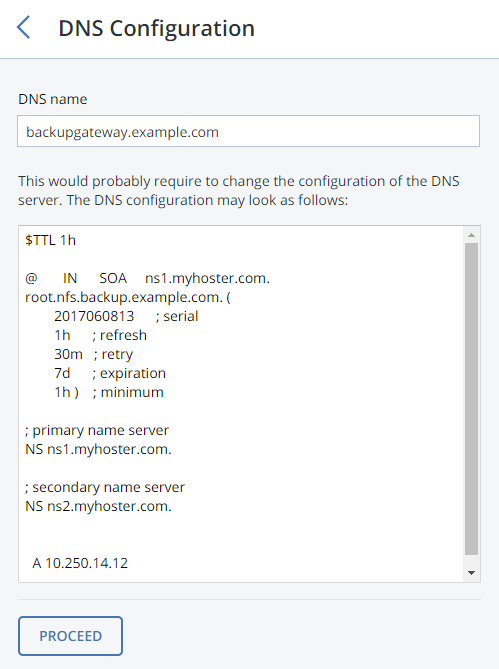
Important
- Configure your DNS server according to the example suggested in the management panel.
- Each time you changes nodes in the Acronis Backup Gateway cluster, adjust the DNS settings accordingly.
Click NEXT.
On the Registration pane, specify the following information for your Acronis product:
- In Account Server Name, specify the address of the Acronis Backup Cloud management portal (e.g., https://cloud.acronis.com/) or the hostname/IP address and port of the Acronis Backup Advanced management server (e.g., http://192.168.1.2:9877).
- In Acronis Account, specify the credentials of a partner account in the cloud or of an organization administrator on the local management server.
Finally, click DONE.
Connecting to Public Cloud Storage via Acronis Backup Gateway¶
With Acronis Backup Gateway, you can have Acronis Backup Cloud or Acronis Backup Advanced store backups in a number of public clouds: Amazon S3, IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, IIJ, Cleversafe, Microsoft Azure, Swift object storage, Softlayer (Swift), Google Cloud Platform, as well as solutions using S3 with the older AuthV2-compatible authentication methods. However, compared to the local Acronis Storage cluster, storing backup data in a public cloud increases the latency of all I/O requests to backups and reduces performance. For this reason, it is recommended to use the local Acronis Storage cluster as storage backend.
Since backups are cold data with specific access rights, it is cost-efficient to use storage classes that are intended for long-term storage of infrequently accessed data. The recommended storage classes include the following:
- Infrequent Access for Amazon S3,
- Cool Blob Storage for Microsoft Azure,
- Nearline and Coldline Storage for Google Cloud Platform.
Note that real data storage costs may be 10-20% higher due to additional fees for operations like data retrieval and early deletion.
Important
- When working with public clouds, Acronis Backup Gateway uses the local storage as the staging area as well as to keep service information. It means that the data to be uploaded to a public cloud is first stored locally and only then sent to the destination. For this reason, it is vital that the local storage is persistent and redundant so the data does not get lost. There are multiple ways to ensure the persistence and redundancy of local storage. You can deploy Acronis Backup Gateway on multiple cluster nodes and select a good redundancy mode. If Acronis Storage with the gateway is deployed on a single physical node, you can make the local storage redundant by replicating it among local disks. If Acronis Storage with the gateway is deployed in a virtual machine, make sure it is made redundant by the virtualization solution it runs on.
- Make sure the local storage cluster has plenty of logical space for staging. For example, if you perform backup daily, provide enough space for at least 1.5 days’ worth of backups. If the daily backup total is 2TB, provide at least 3TB of logical space. The corresponding raw storage required will vary depending on the encoding mode: 9TB (3TB per node) in the mode 1+2, 5TB (1TB per node) in the mode 3+2, etc.
- You must update Acronis Backup Agents to version 12.0.4492 (Windows/Mac) or 12.0.4470 (Linux). Otherwise agents’ attempts to place backups in the new storage backend will result in “Backup failed” errors.
- If you are to store backups in an Amazon S3 cloud, keep in mind that Acronis Backup Gateway may sometimes block access to such backups due to the eventual consistency of Amazon S3. It means that Amazon S3 may occasionally return stale data as it needs time to render the most recent version of the data accessible. Acronis Backup Gateway detects such delays and protects backup integrity by blocking access until the cloud updates.
Before you proceed, make sure that the destination storage has enough space for backups.
To set up Acronis Backup Gateway, do the following:
In the left menu, click SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway.

Select node(s) to run the gateway services on and click Create gateway in the right menu.
Select Public Cloud as storage type.
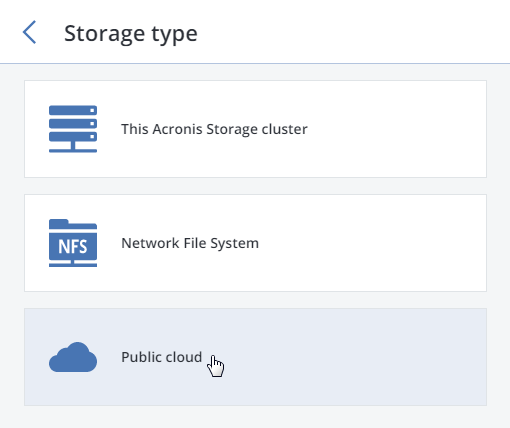
Make sure a network interface with the ABGW private role is selected in the drop-down list. The corresponding interfaces with the ABGW public role will be selected automatically. Click NEXT.
Note
If necessary, click the cogwheel icon and assign the required role(s) to network interfaces on the Network Configuration screen.

On the Public cloud parameters pane, do the following:
- Select a public cloud provider. If your provider is S3-compatible but not in the list, try AuthV2 compatible.
- Depending on the provider, specify Region, Authentication (keystone) URL, or Endpoint URL.
- In case of Swift object storage, specify the authentication protocol version and attributes required by it.
- Specify user credentials. In case of Google Cloud, select a JSON file with keys to upload.
- Specify the folder (bucket, container) to store backups in. The folder must be writeable.
Click NEXT.
On the Registration pane, specify the following information for your Acronis product:
Finally, click DONE.
Migrating Backups from Older Acronis Solutions¶
By means of Acronis Backup Gateway, you can migrate backups from Acronis Storage 1.5 and Acronis Storage Gateway 1.6 and 1.7 to a storage backend of your choice: local storage cluster, external NFS, or public cloud.
Important
- Before you proceed, make sure that the destination storage backend has enough space for both existing and new backups.
- Migration to NFS backends is not available if multiple nodes are selected as Backup Gateway.
The migration procedure can be described as follows:
Root credentials for SSH access to the chosen source storage are provided to Acronis Backup Gateway.
Acronis Backup Gateway sets up a proxy on the source storage that starts redirecting requests incoming from Acronis Backup Agents from the source storage to Acronis Backup Gateway.
Acronis Backup Gateway starts relocating backups to the chosen storage backend. The data that remains to be migrated is shown in the Migration Backlog section on the Acronis Backup Gateway Overview screen. When the backlog empties, all data has been migrated.
After the migration has started, the data of new and incremental backups is stored on the destination storage. Backups from the source storage are pulled in the background. The entire process is transparent to backup agents, which continue working uninterrupted.
To be able to dispose of the source storage after migration completes, requests from Acronis Backup Agents are directed straight to Acronis Backup Gateway, bypassing the proxy on the source storage. Steps that you need to take depend on how the source storage is registered in Acronis Backup Cloud: under the IP address or DNS name.
If the source storage is already registered under the DNS name, you need to change the IP address behind it to those of the Acronis Backup Gateway nodes.
If the source storage is registered under the IP address, it is strongly recommended to re-register Acronis Backup Gateway in Acronis Backup Cloud under a DNS name that resolves into the IP addresses of Acronis Backup Gateway nodes. Using a DNS name will provide a smoother transition and you will not need to reconfigure Acronis Backup Cloud even if you change nodes in the Acronis Backup Gateway (you will still need to adjust the IP addresses behind the DNS name accordingly).
Alternatively, if you do not want to use a DNS name, you need to wait for the migration to complete, shut down both the source and destination machines, and reconfigure your network so that the public interface of the destination machine gets the IP address of the source machine.
The concrete steps that you need to perform in the management panel to initiate backup migration are described in the next subsections.
Migrating Backups from Acronis Storage 1.5¶
Update all Acronis Storage 1.5 nodes to version 1.5.65665 or newer as earlier versions are not eligible for migration. To do this, log in to the Acronis Storage web console, proceed to SETTINGS > Software Update, upload the latest ISO image, and click Update.
Log in to the new Acronis Storage cluster and on the SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway > Nodes screen, select one or more nodes and click Migrate.
Select Acronis Storage 1.5 and click NEXT.
Specify the DNS name of the source storage registered in Acronis Backup Cloud and click NEXT.
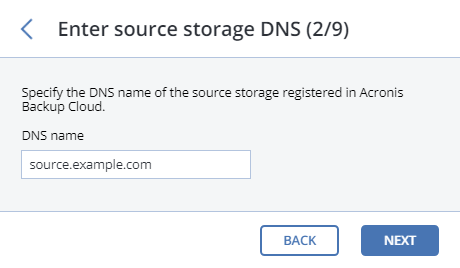
Provide the credentials for the cloud management portal of the Acronis Backup Cloud installation that the source storage is registered in and click NEXT.
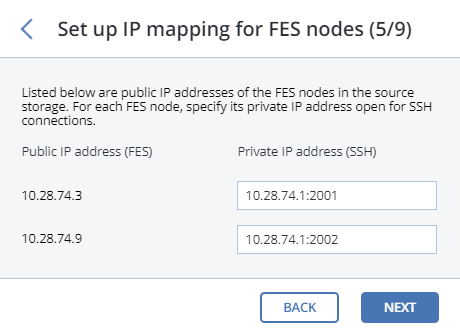
Enable SSH access on all FES nodes of Acronis Storage 1.5 as instructed and click NEXT.
Map the public IP addresses of FES nodes accessible via SSH to their private IP addresses and click NEXT. This step is required to access FES nodes via SSH through tunnels.
Choose a destination storage type to create a gateway to:
- local Acronis Storage cluster,
- external NFS, or
- public cloud.
Make sure a network interface with the ABGW private role is selected in the drop-down list. The corresponding interfaces with the ABGW public role will be selected automatically. Click NEXT.
Note
If necessary, click the cogwheel icon and assign the required role(s) to network interfaces on the Network Configuration screen.

Configure the destination storage backend:
For a storage cluster, select the desired tier, failure domain, and redundancy mode.
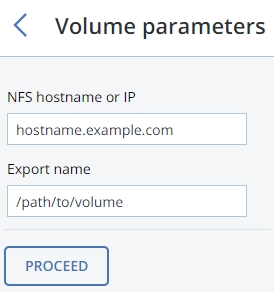
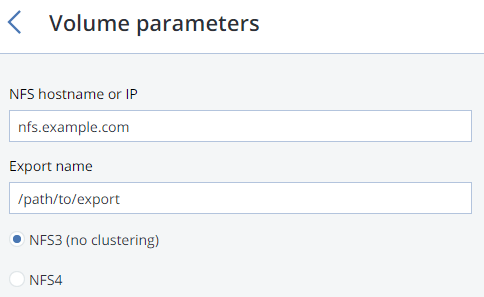
For NFS, specify a hostname or IP address, an export name and path, and choose the NFS version.
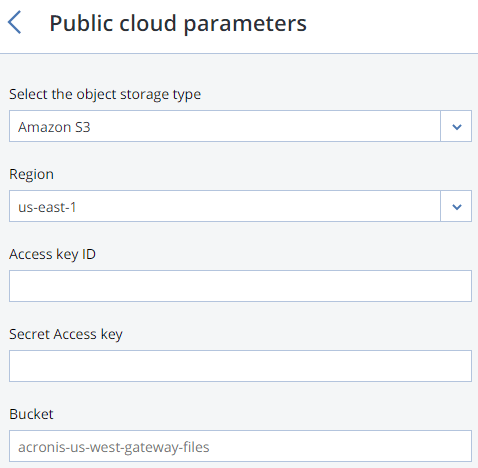
For public cloud, select a public cloud provider, specify credentials, and the name of the folder (bucket, container).
Important
You must update Acronis Backup Agents to version 12.0.4492 (Windows/Mac) or 12.0.4470 (Linux). Otherwise agents’ attempts to place backups in the new storage backend will result in “Backup failed” errors.
Click NEXT.
Review the source and destination storages and click PROCEED.
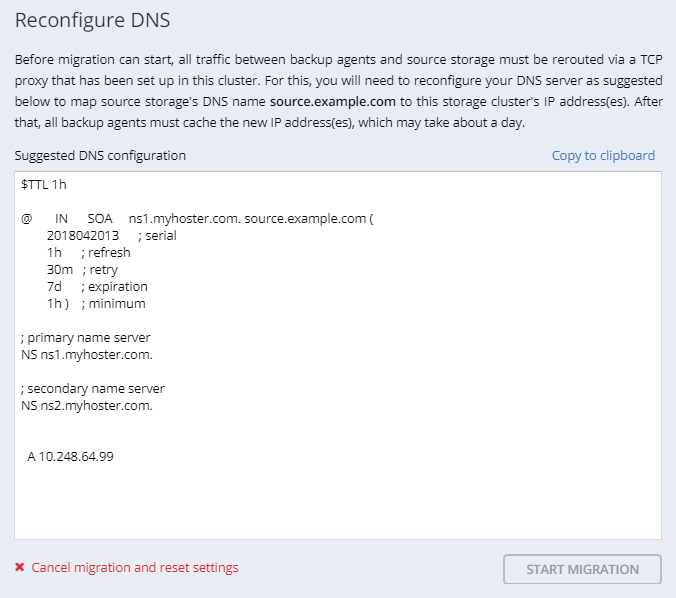
On the next panel, follow the instructions to point the source storage DNS name to the IP addresses of your new Acronis Storage cluster. Having updated the DNS configuration, wait for 24 hours for all backup agents to cache the new IP addresses. Until this happens, the START MIGRATION button will be disabled. After all backup agents have been rerouted to the new cluster, the button will become enabled and you can click it to start migration.
Depending on data size, migration may take as long as several days.
Migrating Backups from Acronis Storage Gateway 1.6 and 1.7 (NFS)¶
Disable the firewall or explicitly open TCP port 44446 on the source Acronis Storage Gateway.
To disable the firewall, run
# systemctl stop firewalld
To open TCP port 44446 in the firewall, do the following:
Find out the zone where port 44445 is open:
# firewall-cmd --list-all-zones | grep active mix_eth0 (active)
Add the required port to the same zone:
# firewall-cmd --zone=mix_eth0 --permanent --add-port=44446/tcp # firewall-cmd --reload
In the management panel of the ABGW node, proceed to SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway > Nodes, select node(s) to run the gateway services on, and click Migrate.
Select the source storage version and click NEXT.
Specify the connection details for the source storage and click NEXT.
Provide the credentials for the cloud management portal of the Acronis Backup Cloud installation that the source storage is registered in and click NEXT.
If the source storage is registered in Acronis Backup Cloud under an IP address, you will see the DNS configuration screen. On it, click RE-REGISTER WITH DNS and specify the source storage DNS name (recommended, see above). Or, if you want to keep using the IP address, click PROCEED WITH IP.
Important
- If you specified a DNS name, configure your DNS server according to the suggested example.
- Each time you change nodes in the Acronis Backup Gateway, adjust the DNS settings accordingly.
Choose a destination storage type to create a gateway to:
- local Acronis Storage cluster,
- external NFS, or
- public cloud.
Make sure a network interface with the ABGW private role is selected in the drop-down list. The corresponding interfaces with the ABGW public role will be selected automatically. Click NEXT.
Note
If necessary, click the cogwheel icon and assign the required role(s) to network interfaces on the Network Configuration screen.

Configure the destination storage backend:
For a storage cluster, select the desired tier, failure domain, and redundancy mode.
For NFS, specify a hostname or IP address, an export name and path, and choose the NFS version.

For public cloud, select a public cloud provider, specify credentials, and the name of the folder (bucket, container).
Important
You must update Acronis Backup Agents to version 12.0.4492 (Windows/Mac) or 12.0.4470 (Linux). Otherwise agents’ attempts to place backups in the new storage backend will result in “Backup failed” errors.

Click NEXT.
Review the source and destination storages and click START MIGRATION.
Depending on data size, migration may take as long as several days.
Monitoring Acronis Backup Gateway¶
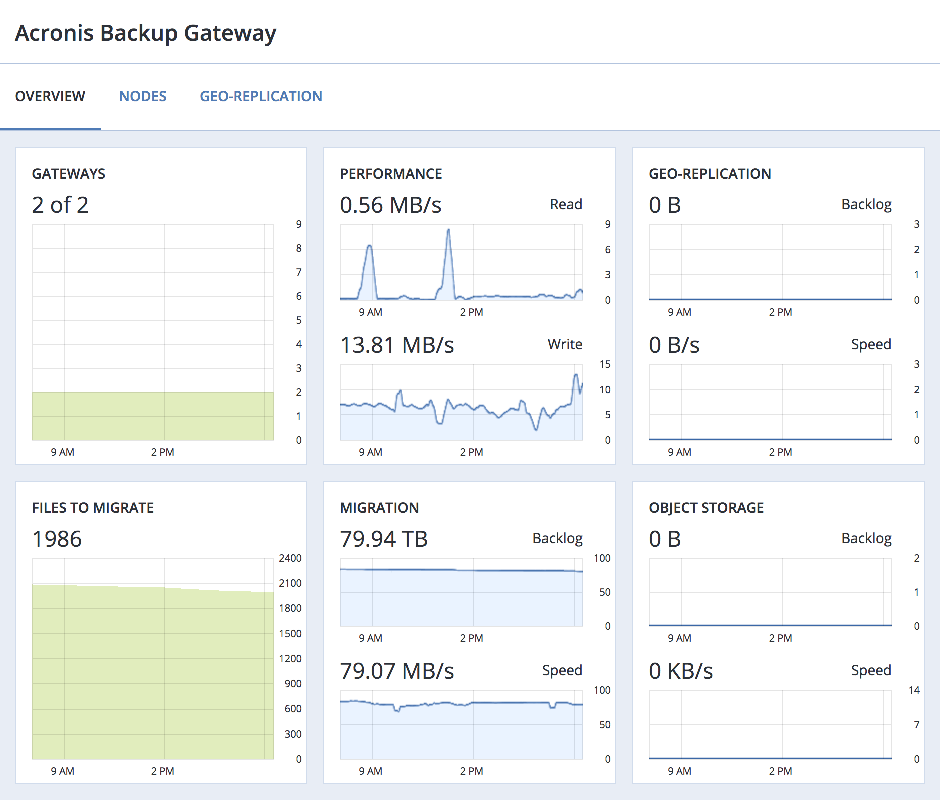
After you create an Acronis Backup Gateway, you can monitor it on the SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway > OVERVIEW screen. The charts show the following information:
- the performance of Acronis Backup Gateway services,
- the geo-replication speed and backlog (the amount of data waiting to be replicated),
- migration speed and backlog (the amount of data waiting to be migrated),
- object storage speed and backlog (the amount of data waiting to be uploaded to public cloud),
- how many files are left in migration queue.
If you migrate backups from Acronis Storage 1.5 or 1.7, migration backlog will be larger than the amount of data on the source storage. The reason is that Acronis Storage versions prior to 2.x use the old backup (FES) protocol that sends more data over network. The difference between source data size and backlog also very much depends on the retention policy utilized by the backup solution. Despite this, the resulting space occupied by migrated data on the destination will be similar to that on the source.
If backlogs do not decrease over time, it means the data cannot be replicated, migrated, or uploaded fast enough. The reason may be insufficient network transfer speed, and you may need to check or upgrade your network.
Releasing Nodes from Acronis Backup Gateway¶
Acronis Backup Gateway is meant to provide access to one specific storage backend. If you need to switch the backend, e.g., from a public cloud to a local Acronis Storage cluster or one public cloud bucket to another, you need to delete the Acronis Backup Gateway by releasing all its nodes and create a new one.
To release one or more nodes from the Acronis Backup Gateway cluster, select them on the SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway > NODES screen and click Release. The Acronis Backup Gateway cluster will remain operational until there is at least one node in it.
Note
When the Acronis Backup Gateway is deleted, it is also unregistered from your Acronis backup software, which loses access to the storage backend.
Do the following to release the last node in the gateway:
On the SERVICES > Acronis Backup Gateway > NODES screen, select the node and click Release.
On the Unregister Acronis Backup Gateway panel, choose one of the following:
Graceful release (recommended, see note below). Releases the node, deletes the Acronis Backup Gateway and unregisters it from your Acronis backup software.
Force release. Releases the node, deletes the Acronis Backup Gateway but does not unregister it from your Acronis backup software.
Important
Choose this option only if you are sure that the gateway has already been unregistered from your Acronis backup software. Otherwise, you will need to register a new gateway in your Acronis backup software and for that you will need to delete and recreate not just the Acronis Backup Gateway but also the entire Acronis Storage cluster.
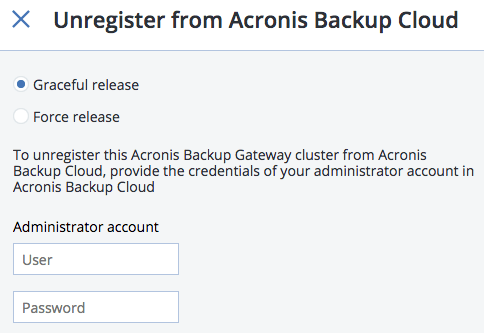
Specify the credentials of your administrator account in your Acronis backup software and click NEXT. In case the release is forced, simply click NEXT.